| Two real world examples: The Simon
Foundation very generously sponsors an |
| effect to build a database of DNA
from 50,000 people with autism spectrum |
|
disabilities. There was a list of 75 genes to be tested for in
2017. This list was
|
| revised to 141 genes in 2019. For
SPARK's current list of genes see |
|
http://spark-sf.s3.amazonaws.com/SPARK_gene_list.pdf |
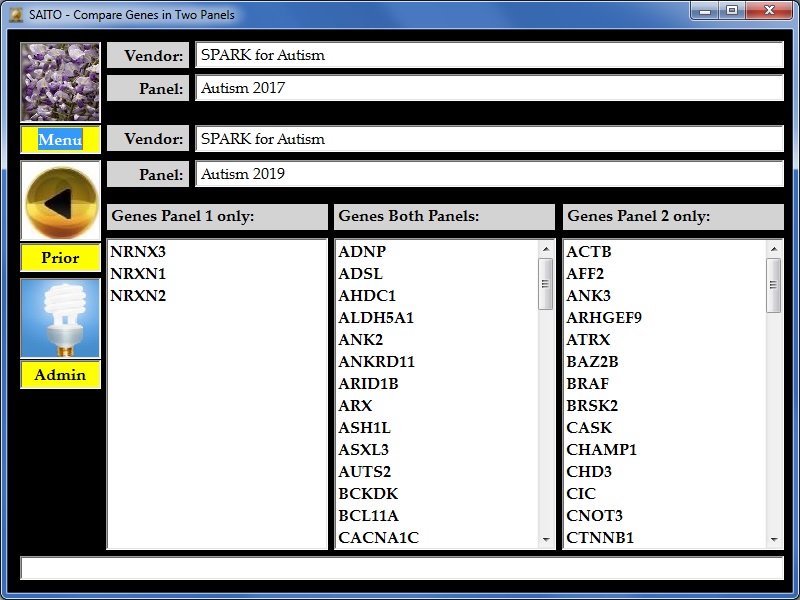 |
| As can be seen
above, a customer with some defect in the one of the three NR |
| genes listed on the left would have
had a diagnosis of somewhere on the autism |
|
spectrum in 2017 but not in 2019. Mutations of NRXN1 are
currently listed as causes |
|
of schizophrenia type 17 and
Pitt-Hopkins-like syndrome 2 (PTHSL2) which is a |
|
syndrome "characterized by severe mental retardation and
variable additional |
|
symptoms, such as impaired speech development,
autistic behavior, breathing |
|
anomalies and a broad mouth, resembling Pitt-Hopkins
syndrome. Other features |
|
include decreased reflexes in the upper extremities,
constipation, strabismus, and |
|
protruding tongue with drooling." In passing, NRXN1
is among the largest human genes. |
| The location of NRXN2 on chromosome
11 is generally agreed, but what exactly it does |
| is the subject of considerable
controversy. I believe NRNX3 is a typographical error
and |
| should be NRXN3. In any case, if
someone tested with one of these three genes in 2017 |
| they might have been diagnosed per
SPARK as autistic but in 2019 they would not be. |
| Likewise, for the list of genes on
the right (beginning with ACTB and AFF2) someone |
| with a damaging variation in one of
those genes would be diagnosed as somewhere on |
| the autism spectrum in 2019 but not
in 2017. I did send SPARK a list of over 500 genes |
| (in addition to their 141) that are
thought to be associated with various autism spectrum |
| disabilities. |
| The actual sequencing for SPARK is
currently done by Prevention Genetics of |
| Marshfield Wisconsin
(www.preventiongenetics.com) - they offer hundreds of tests |
